-
Original Article
-
Development and Validation of a DEM-Based Method for Detecting Topographic Change Areas
DEM등을 활용한 땅밀림 지역의 탐지방법 개발과 검증
-
Seung-Woo Lee, Kye-Won Jun, Nam-Gyun Kim
이승우, 전계원, 김남균
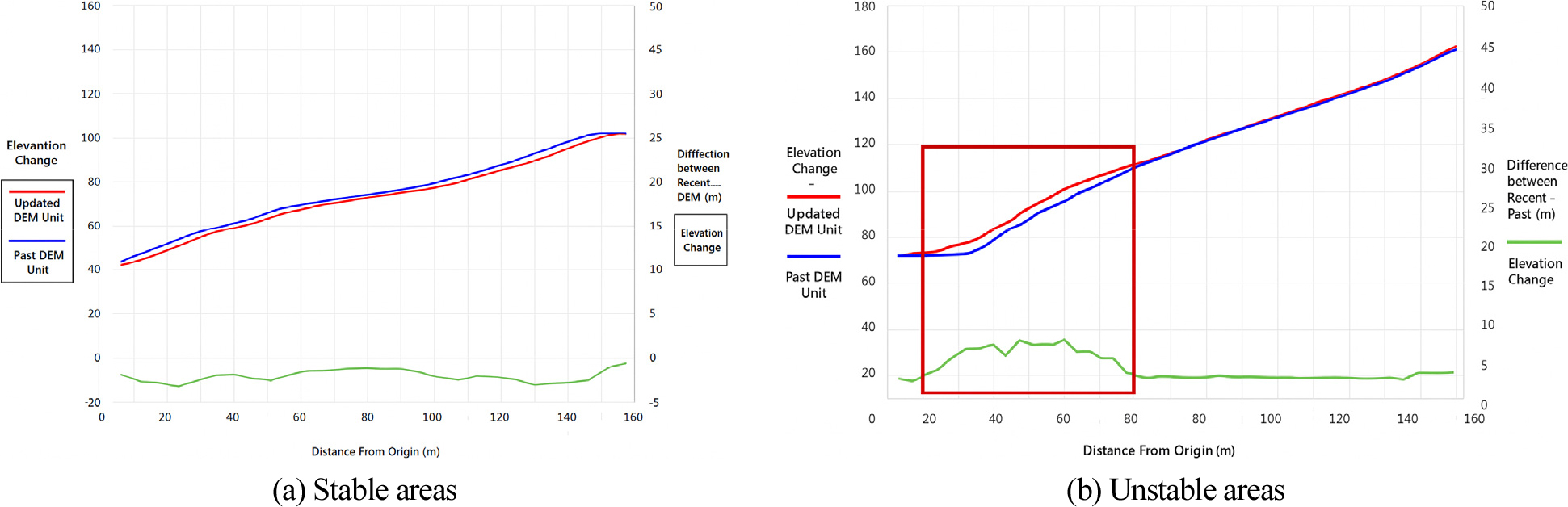
- This study developed an algorithm to analyze land creep hazard zones based on topographic changes in mountainous regions. The proposed algorithm utilized …
본 연구는 산지 지역에서의 지형변화를 기반으로 땅밀림 위험지역을 분석하기 위한 알고리즘을 개발한 것이다. 제안된 알고리즘은 과거와 최신의 수치지형도의 지형, 고도, 곡률을 활용하여 …
- This study developed an algorithm to analyze land creep hazard zones based on topographic changes in mountainous regions. The proposed algorithm utilized both historical and recent digital elevation models (DEMs) to analyze elevation changes, relative displacements, and topographic patterns derived from terrain, altitude, and curvature parameters. By integrating the results from each analytical method, potential topographic deformation zones were identified, and field verification was conducted to confirm the actual occurrence of terrain changes. As a result of applying the developed algorithm model, approximately 112 areas exhibiting significant topographic changes were identified across Gangwon-do Province. Field verification performed at selected sites demonstrated an accuracy of about 22%, thereby validating the preliminary reliability of the proposed algorithm. Further expansion of verification sites is required to enhance reliability, and the incorporation of additional topographic change detection techniques is expected to improve the algorithm’s performance. The refined model is anticipated to be effectively utilized for long-term monitoring and management of deep-seated landslide risks associated with geomorphic evolution.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 산지 지역에서의 지형변화를 기반으로 땅밀림 위험지역을 분석하기 위한 알고리즘을 개발한 것이다. 제안된 알고리즘은 과거와 최신의 수치지형도의 지형, 고도, 곡률을 활용하여 표고변화량, 상대변위량, 지형 패턴을 분석하였다. 각각의 방법으로 분석된 대상지를 종합적으로 검토하여 지형변화 위험지역을 선별하였고, 현장검증을 통해 실제 지형변화 발생지역 여부를 검증하고자 하였다. 본 연구를 통해 개발된 알고리즘 모델을 적용한 결과, 강원도 내 약 112개소의 지형변화 지역을 도출하였으며, 그 중 일부 지역에 대해 현장검증을 실시한 결과 약 22% 정도 정확도로 알고리즘의 타당성을 검증하였다. 향후에는 검증지역을 확대하여 신뢰성을 추가로 검증할 필요가 있으며, 지형변화 탐지 기법을 추가 개발하여 기존 알고리즘을 고도화시킬 경우, 장기적인 지형변화에 따른 땅밀림 위험성 관리에 효과적으로 활용될 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
-
Development and Validation of a DEM-Based Method for Detecting Topographic Change Areas
-
Original Article
-
A Study on Predicting Coastal Wave Arrival along the South Korea Southern Coast under Nankai Earthquake Scenarios Using a Generative AI Platform
생성형 AI 플랫폼을 활용한 난카이 지진 시나리오에서 남해안의 도달 파도 예측 연구
-
Sungkwon Baek, Jaehyeung Jeoung
백성권, 정재형
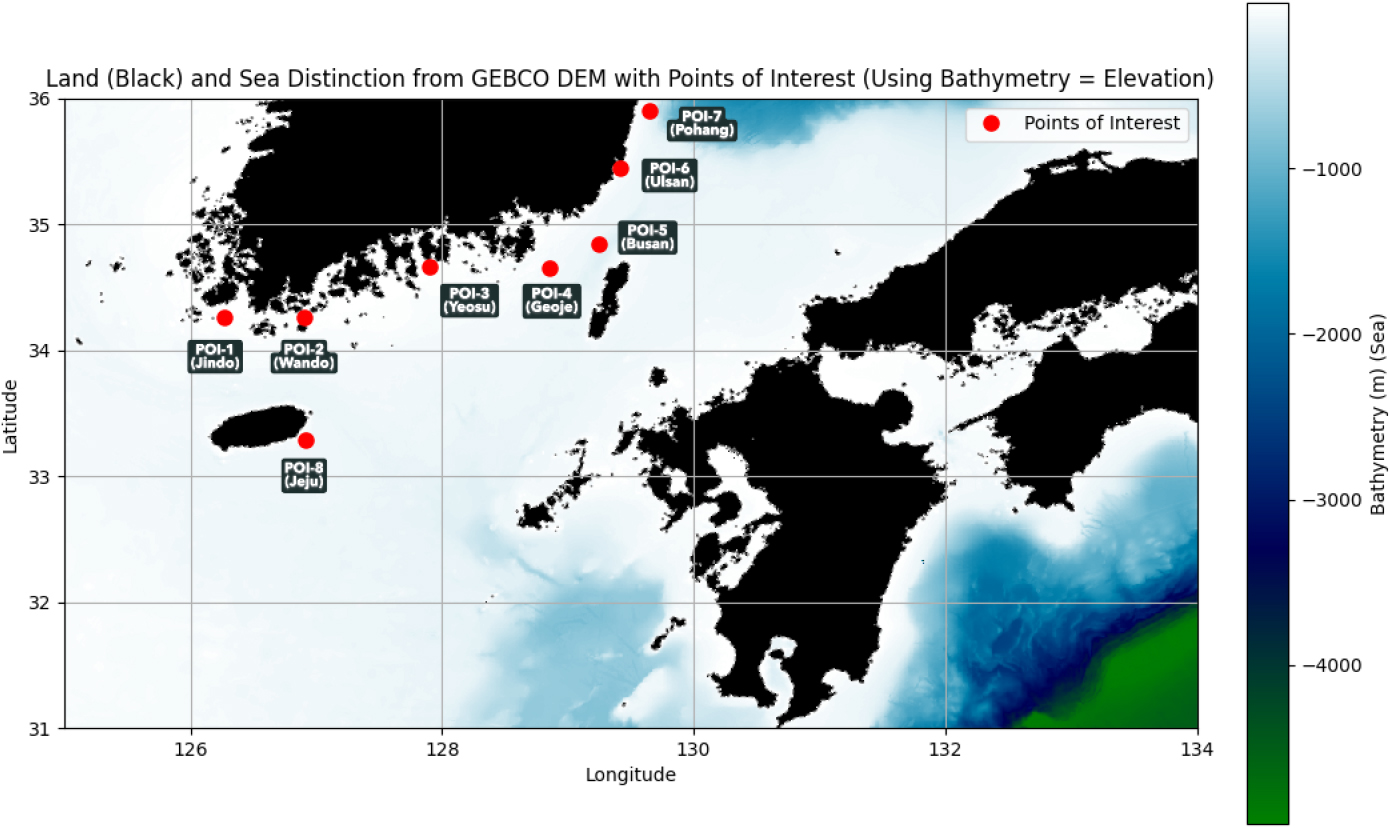
- This study investigates tsunami propagation and wave arrival characteristics along the southern coast of Korea and Jeju Island, generated by a potential …
본 연구는 일본 난카이 해곡에서 발생 가능한 대규모 지진(Mw 9.1)을 대상으로, 생성형 인공지능(AI) 플랫폼을 활용하여 남해안 및 제주 연안에 도달하는 쓰나미의 전파 …
- This study investigates tsunami propagation and wave arrival characteristics along the southern coast of Korea and Jeju Island, generated by a potential large-scale Nankai Trough earthquake (Mw 9.1), using a generative artificial intelligence (AI) platform. The AI framework, based on the linear shallow-water approximation and travel-time integration method, performed automated multi-scenario calculations, uncertainty quantification, and rapid prediction for 11 distributed fault scenarios. Three analytical approaches—Case 1 (single Okada model), Case 2 (multi-scenario ensemble), and Case 3 (Tohoku observation-based correction)—were compared. The results show tsunami arrival times of approximately 4–7 hours and maximum wave heights mostly below 1.0 m at major southern coastal ports. The corrected Case 3 results demonstrated strong agreement with existing observational and numerical model data. This study suggests that AI-based approximate modeling can serve as a practical tool for preliminary assessments and early-warning support.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 일본 난카이 해곡에서 발생 가능한 대규모 지진(Mw 9.1)을 대상으로, 생성형 인공지능(AI) 플랫폼을 활용하여 남해안 및 제주 연안에 도달하는 쓰나미의 전파 특성과 도달 파고를 예측하였다. AI 플랫폼은 선형 천수파 근사와 도달시간 적분법을 기반으로 하여, 11개 분포형 단층 시나리오의 자동 계산, 불확실성 정량화, 신속 예측을 수행하였다. 해석은 Case 1(단일 Okada 해석), Case 2(다중 시나리오 앙상블), Case 3(도호쿠 실측 보정)의 세 가지 접근법으로 비교되었다. 결과적으로 남해안 주요 항만의 쓰나미 도달시간은 약 4–7시간, 최대 파고는 대부분 1.0 m 이하로 나타났다. Case 3 보정 결과는 기존 관측자료 및 수치모델 결과와 높은 일치성을 보였다. 본 연구는 생성형 AI 기반 근사 해석이 실무적 사전 검토 및 조기경보 지원 도구로 활용될 수 있음을 제시하였다.
-
A Study on Predicting Coastal Wave Arrival along the South Korea Southern Coast under Nankai Earthquake Scenarios Using a Generative AI Platform
-
Original Article
-
Numerical Simulation of Tsunami Generation and Propagation Induced by Underwater Explosions
수중 폭발로 유발된 해일의 발생 및 전파 특성 수치해석
-
Jaehwan Kim, Sarki Park, Dong-Woo Seo
김재환, 박상기, 서동우
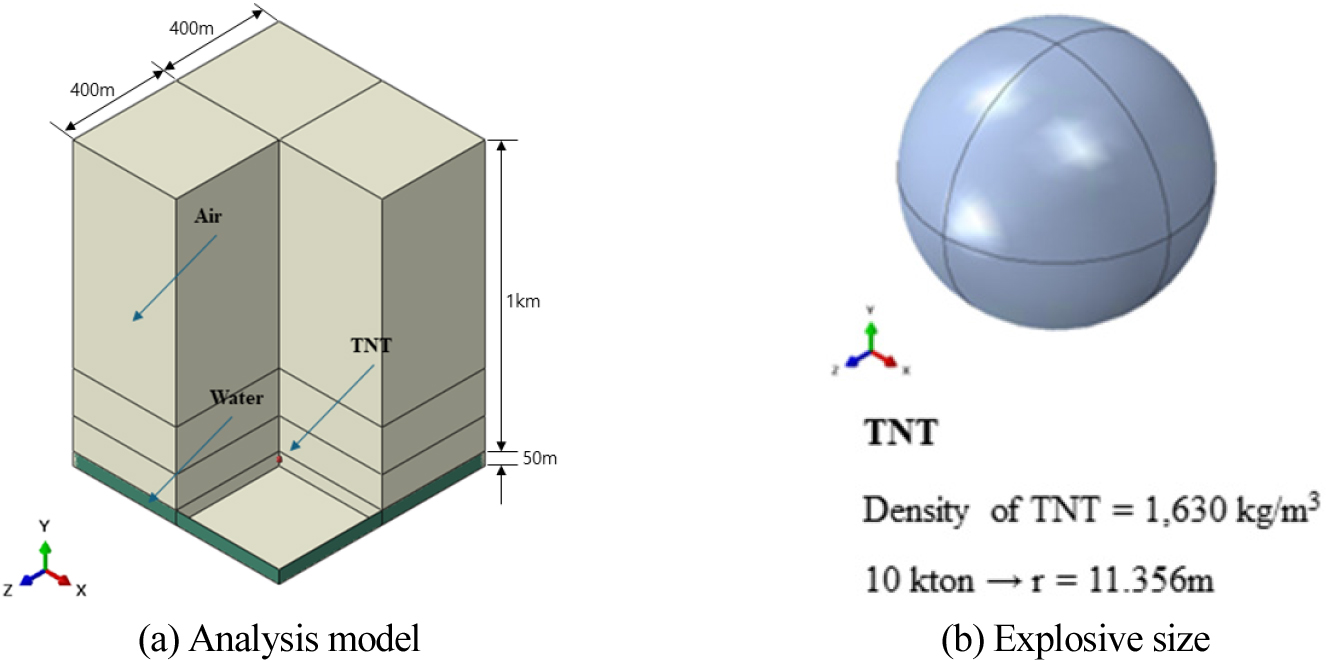
- This study analyzed the generation and propagation characteristics of tsunamis induced by underwater explosions using numerical simulation, aiming to provide fundamental data …
본 연구는 수중 폭발이라는 극한 상황에서 발생하는 해일에 대한 발생 및 전파 특성을 수치해석으로 분석하여 해상 구조물의 피해를 예측하기 위한 기초 데이터를 …
- This study analyzed the generation and propagation characteristics of tsunamis induced by underwater explosions using numerical simulation, aiming to provide fundamental data for assessing potential damage to maritime structures. A two-phase analysis was performed using the Coupled Eulerian-Lagrangian (CEL) technique in ABAQUS. In Phase 1, the water column size (height
H
0
and equivalent width
W
0
) was quantified based on explosion depth for a 10 kton TNT equivalent explosion, confirming that the water column height increased with depth. Phase 2 modeled tsunami propagation using the dam-break principle and derived a regression equation to predict the maximum coastal wave height based on the initial water column dimensions. The simulation results predicted a maximum wave height of up to 32 m and an average flow velocity of 30 m/s at the coast. This quantitative data provides essential information for disaster preparedness and damage assessment of key maritime structures such as cable-stayed bridges.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 수중 폭발이라는 극한 상황에서 발생하는 해일에 대한 발생 및 전파 특성을 수치해석으로 분석하여 해상 구조물의 피해를 예측하기 위한 기초 데이터를 확보하는데 목적이 있다. 해석 신뢰도를 높이기 위하여 ABAQUS의 CEL(Coupled Eulerian-Lagrangian) 기법을 활용하여 2단계의 수치 시뮬레이션을 수행하였다. 1단계 해석에서는 10 kton TNT 등가 폭발 시나리오에서 폭발 수심 변화(15, 25, 35 m)에 따른 물기둥의 규모(높이 H 0 및 등가 환산폭 W 0 )를 정량적으로 분석하였으며, 폭발 수심이 깊어질수록 물기둥 높이가 증가하는 경향을 확인하였다. 2단계 해석 1단계에서 도출된 물기둥 데이터를 초기조건으로 설정하고 댐-붕괴 이론을 적용하여 해일의 전파 과정을 모사하였다. 이를 바탕으로 물기둥 초기 규모와 해안가 최대 해일 높이 간의 예측 회귀식을 도출하였다. 시뮬레이션 결과, 대상 조건에서 해안가에 도달하는 해일 최대 높이는 약 32 m, 평균 유속은 30 m/s로 예측되었다. 이러한 정량적 데이터는 케이블지지 교량과 같은 주요 해상 구조물의 재난 대비 및 피해 규모 산정을 위한 기초 자료로 활용될 수 있을 것이다.
-
Numerical Simulation of Tsunami Generation and Propagation Induced by Underwater Explosions
-
Case Study
-
A Case Study on Hazard Assessment of Ground Creep Areas Based on Geophysical Exploration
물리탐사 기반의 땅밀림 지역 위험성평가 사례연구
-
Seung-Woo Lee, Kye-Won Jun
이승우, 전계원
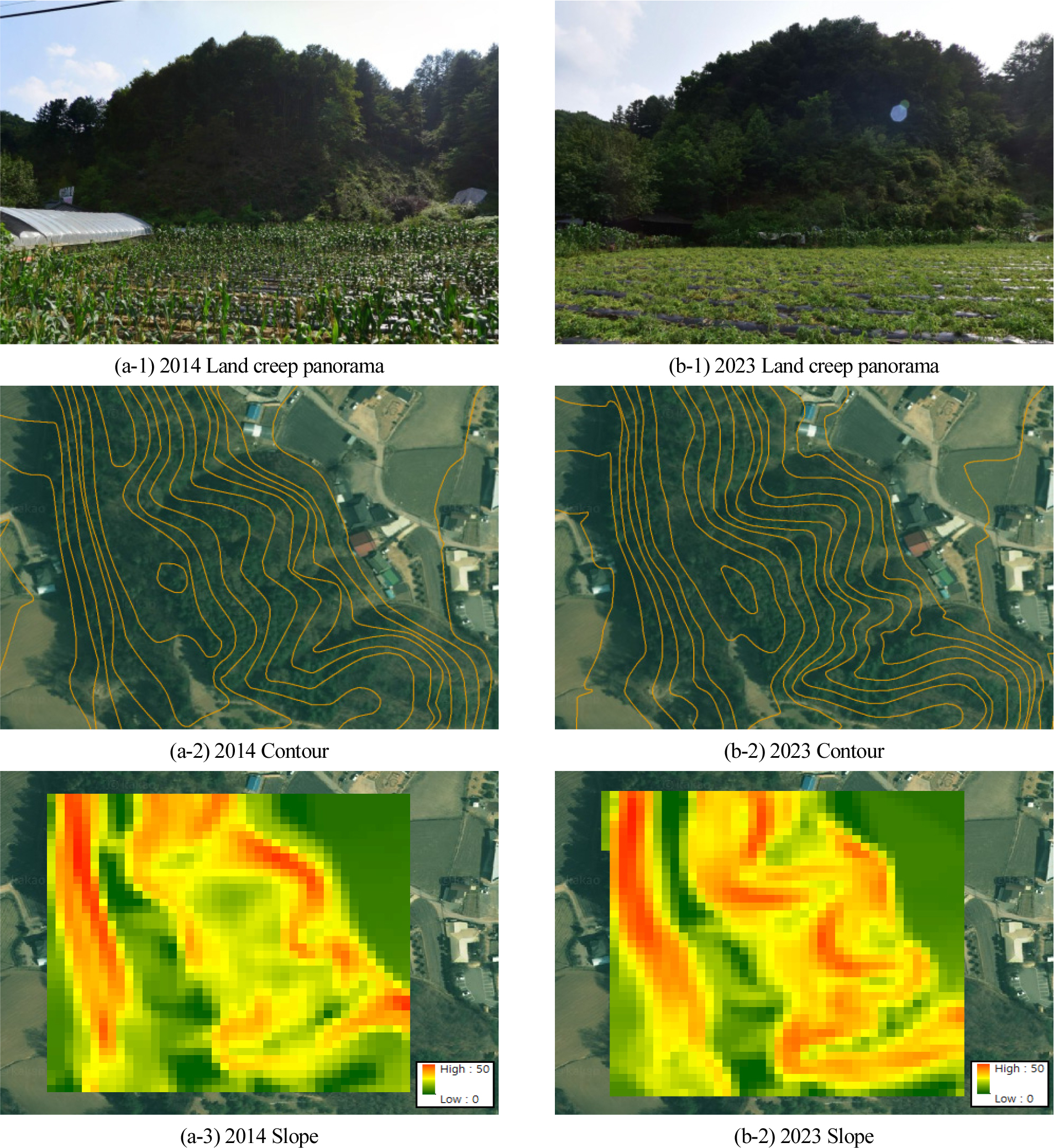
- This study quantitatively analyzed the characteristics of areas affected by land creep through geophysical survey. To assess the scale of the land …
본 연구에서는 물리탐사를 통하여 땅밀림이 발생하는 지역의 특징을 정량적으로 분석하였다. 땅밀림의 규모를 파악하기 위하여 상단부, 중단부, 하단부로 구분하여 지질, 토양, 지형, 수리, …
- This study quantitatively analyzed the characteristics of areas affected by land creep through geophysical survey. To assess the scale of the land creep, the site was divided into upper, middle, and lower sections, and investigations were conducted on geological, soil, topographical, hydrological, and forest characteristics. Soil samples were collected and tested in the laboratory to determine soil properties such as moisture content, internal friction angle, and permeability coefficient. In addition, seismic and electrical resistivity surveys were conducted to analyze subsurface characteristics. Using these data, slope stability analyses were performed to evaluate the risk of ground failure during both dry and rainy seasons, thereby assessing the likelihood of collapse due to soil creep. The study site was a slope in Wongil-ri, Bongpyeong-myeon, Pyeongchang-gun, Gangwon-do, where soil creep is actively occurring. Although the land creep is not easily identifiable by visual inspection, the creeping area was found to be uplifted weathered bedrock at the lower slope, and it was determined to be at risk of collapse during the rainy season. Through multiple geophysical investigations, this study identified the characteristics of creeping slopes and suggests that these findings can inform effective risk management strategies for such areas.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구에서는 물리탐사를 통하여 땅밀림이 발생하는 지역의 특징을 정량적으로 분석하였다. 땅밀림의 규모를 파악하기 위하여 상단부, 중단부, 하단부로 구분하여 지질, 토양, 지형, 수리, 산림 특성을 조사하였다. 토질 시료를 채취하여 실내실험을 통해 함수율, 마찰각, 투수계수 등의 토질 특성의 값을 추출하고, 탄성파 탐사와 전기비저항 탐사를 통해 지반구조의 특성을 분석하였다. 이러한 값들을 이용해 사면안정해석을 수행하여 건기와 우기시의 지반 붕괴 위험성을 평가하여 땅밀림으로 인한 붕괴 여부를 판단하였다. 위험성 평가 대상지는 강원도 평창군 봉평면 원길리의 사면으로 땅밀림이 발생한 지역이다. 대상지는 육안으로 구분하기 어려운 땅밀림 지역으로 사면 하부의 풍화암층이 솟아오른 것으로 분석되었으며 우기시 붕괴가 가능한 지역인 것으로 분석되었다. 이러한 땅밀림 지역에 대한 다수의 물리탐사를 통해 땅밀림의 특성을 규명하여 붕괴 위험성에 대한 관리방안을 제시할 수 있을 것으로 판단된다.
-
A Case Study on Hazard Assessment of Ground Creep Areas Based on Geophysical Exploration
-
Original Article
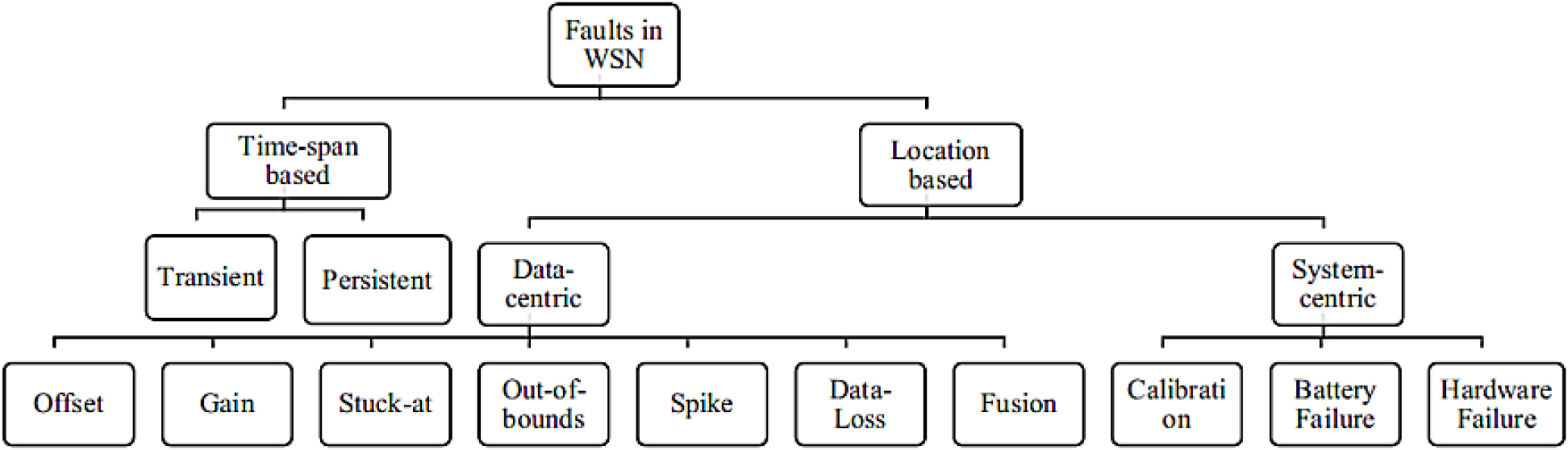
-
Data Fault Detection of Structural Health Monitoring System (SHMS)
구조 건전성 모니터링 데이터의 결함 검출 기법 고찰
-
Jaehwan Kim, Wook Kim, Heesoo Son, Hojin Kim
김재환, 김욱, 손희수, 김호진
- In recent years, the application of Structural Health Monitoring (SHM) technology has rapidly expanded to enhance the long-term safety and maintenance efficiency …
최근 구조물의 장기 안전성 활보와 유지관리 효율향상을 위해 구조 건전성 모니터링(Structural Health Monitoring) 기술의 적용이 급격히 확대되고 있다. 해당 모니터링 시스템의 센서 …
- In recent years, the application of Structural Health Monitoring (SHM) technology has rapidly expanded to enhance the long-term safety and maintenance efficiency of civil infrastructure. The large-scale data collected from sensor networks in such monitoring systems may contain various types of faults—such as sensor malfunction, signal drift, data loss, and noise contamination—which can significantly degrade the reliability of structural condition assessments. This study comprehensively investigates both data-driven and model-based approaches for the early detection of data faults acquired from Structural Health Monitoring Systems (SHMS). Statistical anomaly detection methods, frequency-domain analyses, machine learning algorithms, and hybrid fault detection techniques were examined to compare their strengths and limitations. The comparative evaluation also assessed the practical applicability of these methods to bridge monitoring systems and digital sensing networks.
- COLLAPSE
최근 구조물의 장기 안전성 활보와 유지관리 효율향상을 위해 구조 건전성 모니터링(Structural Health Monitoring) 기술의 적용이 급격히 확대되고 있다. 해당 모니터링 시스템의 센서 네트워크로부터 수집되는 대용량 데이터에는 센서의 기능이상, 신호 디르프, 데이터 손실, 노이즈 혼입 등 다양한 결함(Fault)이 존재할 수 있으며, 이는 구조 상태 진단 결과의 신뢰성을 심각하게 저하시킬 수 있다. 본 연구는 구조 건전성 모니터링 시스템(SHMS)으로부터 취득된 데이터 결함을 조기 검출하기 위한 데이터 중심(Data-driven) 및 시스템 중심(Model-based)기법을 종합적으로 검토하였고 통계적 이상치 검출, 주파스 분석, 머신러닝 및 하이브리드 결함 검출 알고리즘을 고찰하여 그 장, 단점을 비교분석하여 교량 및 디지털 센싱, 네트워크 적용에 대한 실효성을 분석하였다.
-
Data Fault Detection of Structural Health Monitoring System (SHMS)
-
Original Article
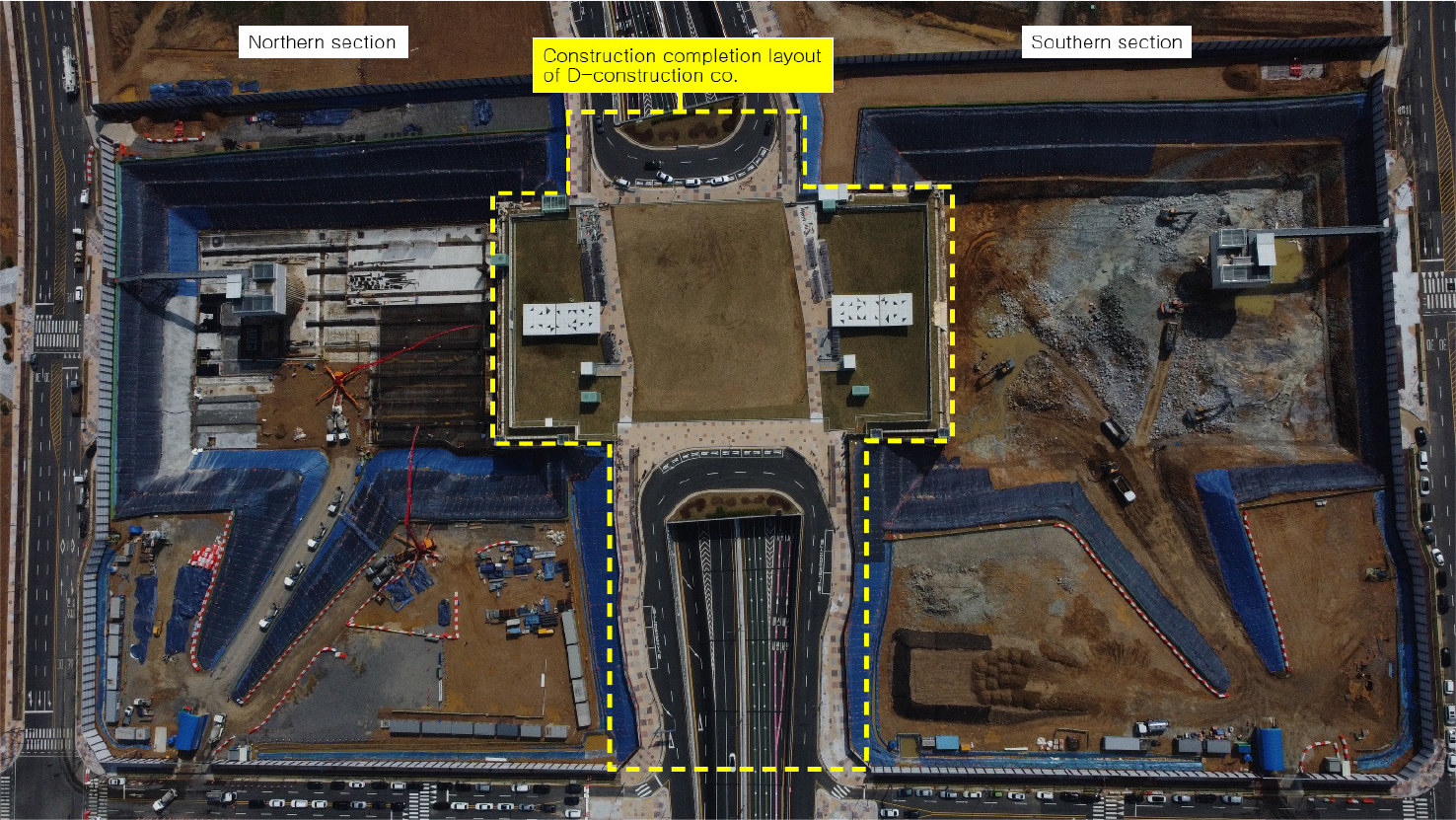
-
A Study on the Application of the Project in the Safety Work Division Structure of Construction Management Service
건설사업관리용역 안전업무분할체계의 프로젝트 적용사례에 관한 연구
-
Sung-Soo Kim
김성수
- Construction project management engineers perform their work in accordance with relevant guidelines and laws based on construction project management services and business …
건설사업관리기술인은 건설사업관리용역과업내용서를 기준으로 관련 지침과 법령에 따라 업무를 수행한다. 발주자에 대한 지식과 경험에 따라 업무를 이해하고 수행하는 방법이 상이하여 결과물을 도출하는데 많은 …
- Construction project management engineers perform their work in accordance with relevant guidelines and laws based on construction project management services and business contents. It takes a lot of time to derive the results because the method of understanding and performing the work is different depending on the knowledge and experience of the person placing an order. Based on the “Construction Project Management Service Task Description and Safety Management Guidelines, including the Construction Stage Supervision Authority of Paju Unjeongjungang GTX-A Station Transfer Parking Lot Construction,” this paper introduces the order and detailed method of writing the safety work division system, and even presents standardization cases. After applying it to various projects in the future, re-establishing the division system and revising the relevant laws in a timely manner to maximize work productivity and suggest active use of safety construction project management engineer.
- COLLAPSE
건설사업관리기술인은 건설사업관리용역과업내용서를 기준으로 관련 지침과 법령에 따라 업무를 수행한다. 발주자에 대한 지식과 경험에 따라 업무를 이해하고 수행하는 방법이 상이하여 결과물을 도출하는데 많은 시간이 소요된다. 본 연구에서는 “파주 운정중앙역 GTX-A 환승주차장건설공사의 시공단계 감독권한대행 등 건설사업관리용역 과업내용서와 안전관리지침”을 기준으로 안전업무 분할체계 작성순서와 상세 작성방법을 소개하고, 표준화사례까지 제시합니다. 향후 다양한 프로젝트에 적용한 후 업무분할체계를 재정립하고 관계법령의 제개정 시 적기에 수정하여 활용하면 업무생산성을 향상시킬 수 있으며, 안전건설사업관리기술인의 적극적인 활용을 제언합니다.
-
A Study on the Application of the Project in the Safety Work Division Structure of Construction Management Service
-
Original Article
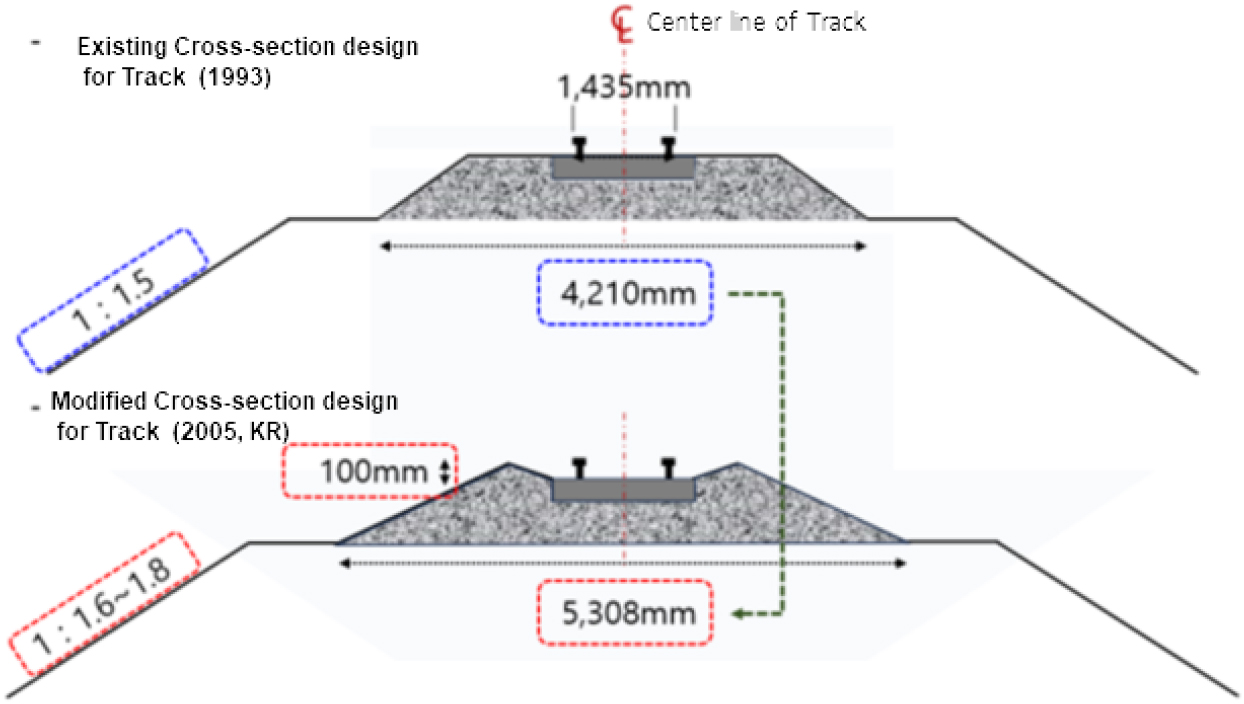
-
Development and Verification of a Railway Precast Concrete Sidewalk System
철도 프리캐스트 점검로 시스템 개발 및 성능 검증
-
Kyu-San Jung, Sangki Park, Jung-Hyun Kim, Hoe-Chang Choe, Dong-Woo Seo
정규산, 박상기, 김정현, 최회창, 서동우
- This study concerns the development of a precast railway inspection sidewalk system designed to enhance maintenance efficiency and ensure safety by enabling …
본 연구는 철도 유지관리 효율성 증대 및 안전 확보를 목적으로 작업자의 안전한 대피 및 이동 그리고 도상유실방지가 가능한 프리캐스트 철도 점검로 개발에 …
- This study concerns the development of a precast railway inspection sidewalk system designed to enhance maintenance efficiency and ensure safety by enabling workers’ safe evacuation and movement while preventing track bed erosion. This paper introduces the construction method for a lightweight precast inspection walkway system capable of rapid installation and presents experimental results verifying its performance. Railway maintenance and reinforcement work is primarily conducted at night within the limited timeframe of train blockage periods. Ensuring worker safety during operations conducted while trains are running is particularly critical. The precast inspection sidewalk developed in this study enables rapid construction and is expected to contribute to securing safe movement paths for maintenance personnel in the future. This construction method involves transporting equipment to the site using a trolley and precast components, forming the support structure via the helical pile method, and installing the precast concrete superstructure. Construction feasibility was confirmed through indoor and field performance verification tests. Furthermore, experiments are underway to increase the span length of the superstructure from 1 m to 3 m, aiming to minimize foundation pile work, reduce costs, and shorten construction duration. This research is expected to significantly advance railway maintenance by overcoming the limitations of existing inspection walkway construction methods.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 철도 유지관리 효율성 증대 및 안전 확보를 목적으로 작업자의 안전한 대피 및 이동 그리고 도상유실방지가 가능한 프리캐스트 철도 점검로 개발에 관한 내용이다. 본 논문에서는 급속 시공이 가능한 저중량 프리캐스트 점검로의 공법을 소개하고, 성능 검증에 관한 실험적 결과를 제시하고자 한다. 철도 보수·보강 등 유지관리 공사는 주로 야간에 열차 차단 시간 내에 제한된 시간 내에 작업이 수행된다. 열차가 운행 중인 시간의 작업은 특히 작업자의 안전확보가 매우 중요하다. 본 연구에서 개발한 프리캐스트 점검로는 신속한 시공이 가능하여, 향후 유지관리 작업자의 안전 확보를 위한 이동 경로 확보 등에 이바지할 것으로 기대된다. 본 공법은 트롤리를 이용한 장비와 프리캐스트 부재의 현장 진입 후, 헬리켈 파일 작업을 통하여 지지대를 형성하고 프리캐스트 콘크리트 상부 구조체를 배치하여 시공되는 공법이다. 현재 실내외 성능 검증 실험을 통하여 시공성을 확인하였다. 또한, 상부 구조의 장경간화를 위한 실험을 실시하여 기초 파일 작업의 감소를 통하여 경제성과 공기 단축을 이루고자 한다. 본 연구는 기존의 점검로 관련 공법들이 갖는 한계를 넘어 철도 유지관리에 큰 역할을 할 것으로 기대된다.
-
Development and Verification of a Railway Precast Concrete Sidewalk System
-
Original Article
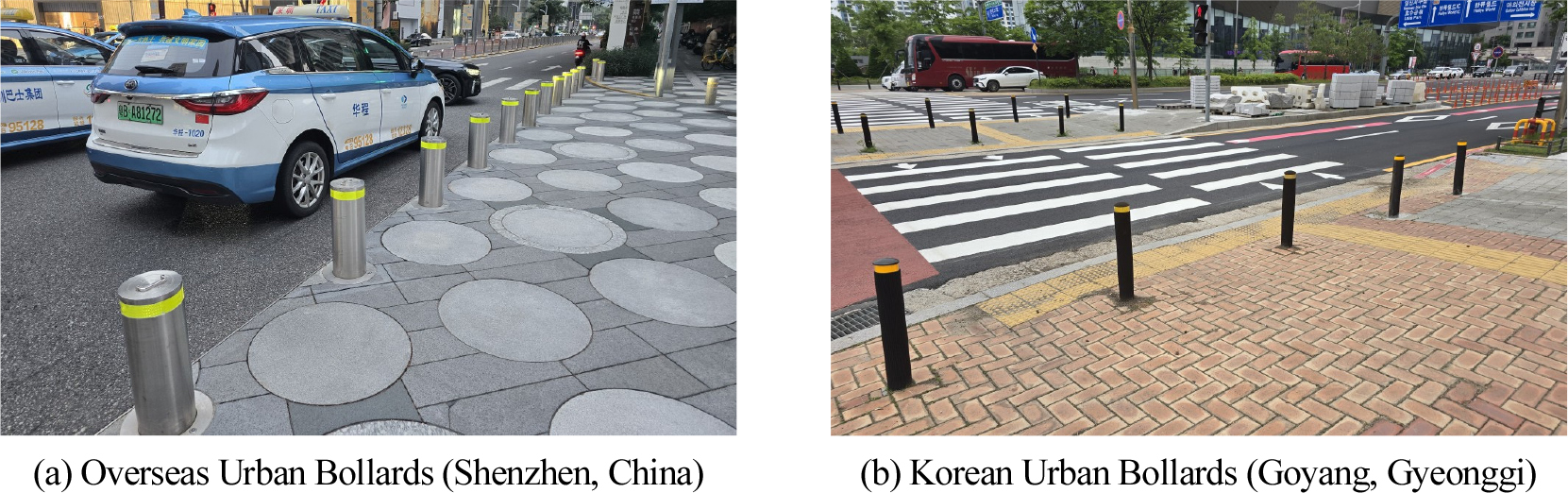
-
Proposal of Performance Standards for Bollards for Urban Sidewalk Safety
도심 보도 안전을 위한 방호말뚝(볼라드) 성능 기준 제안
-
Bong-Chul Joo, Kwang-Sup Son, Sung-Jin Lee, Jun-Ki Hong
주봉철, 손광섭, 이성진, 홍준기
- This study aims to contribute to the development of performance evaluation standards in Korea for protective piles installed to ensure pedestrian safety …
본 연구는 보도를 침범하는 차량으로부터 보행자의 안전을 확보하기 위해 설치하는 방호말뚝에 대한 국내 성능평가 기준을 정비하는데 이바지하고자 방호말뚝 관련 국제 성능 기준인 …
- This study aims to contribute to the development of performance evaluation standards in Korea for protective piles installed to ensure pedestrian safety from vehicles encroaching on sidewalks. To this end, we analyzed international performance standards for protective piles, such as the US ASTM F2656 and ASTM F3016, the European ISO 22343-1, and the Japanese Bollard Installation Manual. We then proposed a draft protective performance standard suitable for urban road environment in Korea. The proposed performance standards for protective bollards were established in consideration of international standards. Crash test conditions were established considering domestic urban road speed limits and major vehicle types driving in urban areas. Furthermore, performance evaluation criteria suitable for the domestic urban environment were proposed, taking into account factors such as the effective width of urban sidewalks.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 보도를 침범하는 차량으로부터 보행자의 안전을 확보하기 위해 설치하는 방호말뚝에 대한 국내 성능평가 기준을 정비하는데 이바지하고자 방호말뚝 관련 국제 성능 기준인 미국 ASTM F2656, ASTM F3016 및 유럽 ISO 22343-1와 일본 볼라드 설치편람을 분석하고, 국내 도심 도로 환경에 적합한 방호성능기준(안)을 제시하였다. 제안된 방호말뚝의 성능기준은 국제표준과의 연계를 고려하였으며, 국내 도심 도로 제한속도와 도심에서 주행하는 주요 차량 종류를 고려하여 충돌시험 조건을 설정하였고, 도심 보도 유효 폭 등을 고려하여 국내 도심 환경에 적합한 성능 평가 기준을 제시하였다.
-
Proposal of Performance Standards for Bollards for Urban Sidewalk Safety
-
Original Article
-
A Study on the Design of Gateway and Communication System for Intelligent Safety Module in Power Facility Maintenance Vehicles
전력설비 유지보수 차량을 위한 지능형 안전 모듈의 게이트웨이 및 통신 시스템 설계에 관한 연구
-
Dong-Yeop Lee, Hyeong-Gyoon Park, Dong-Min Kim, Eun-Seong Go, Jun-Ho Bang
이동엽, 박형균, 김동민, 고은성, 방준호
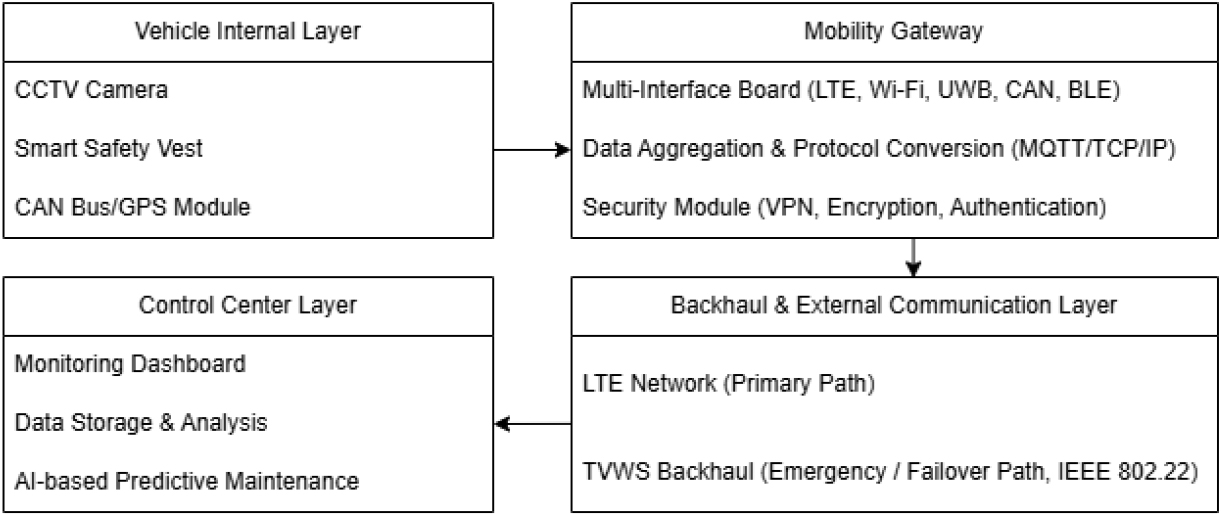
- This study proposes a multi-interface gateway and a dual backhaul communication architecture to enhance real-time safety monitoring and communication reliability of power …
본 연구에서는 전력설비 유지보수 차량의 실시간 안전 관리 및 통신 안정성 확보를 위해 다중 통신 기반 게이트웨이 및 백홀 구조를 제안하였다. 게이트웨이는 …
- This study proposes a multi-interface gateway and a dual backhaul communication architecture to enhance real-time safety monitoring and communication reliability of power maintenance vehicles. The proposed gateway integrates LTE, UWB, CAN, GPS, and Wi-Fi/BLE interfaces to collect in-vehicle data and transmits them securely to the control center using MQTT-based telemetry and VPN encryption. Moreover, a failover mechanism from LTE to TV White Space (TVWS) is applied to maintain communication continuity under LTE degradation or outage. A prototype gateway board was implemented and validated through functional and performance evaluations. Experimental results confirmed that key performance metrics—latency, throughput, packet delivery, and VPN session continuity—meet operational requirements, demonstrating stable data transmission even during LTE-to-TVWS switchover. This work provides a practical foundation for deploying intelligent safety and monitoring systems for power maintenance vehicles. Future work includes field-level validation in real operation environments and performance improvement for long-term stability.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구에서는 전력설비 유지보수 차량의 실시간 안전 관리 및 통신 안정성 확보를 위해 다중 통신 기반 게이트웨이 및 백홀 구조를 제안하였다. 게이트웨이는 LTE, UWB, CAN, GPS, Wi-Fi/BLE 인터페이스를 통합하여 차량 내부 데이터를 수집하며, MQTT 기반 Telemetry 송신, 보안 기반 VPN 전송을 적용하여 데이터 전송의 무결성과 신뢰성을 확보하였다. 또한 LTE 장애 발생 시 TVWS 기반으로 자동 전환되는 이중 백홀 구조를 통해 통신 연속성을 유지하도록 설계하였다. 제작된 프로토타입 게이트웨이 보드를 활용하여 데이터 송수신 기능과 성능 검증을 수행하였으며, 실험 결과 데이터 지연, 처리량, VPN 세션 연속성 등 주요 지표가 요구 기준을 만족함을 확인하였다. 특히 LTE→TVWS 전환 시에도 세션이 유지되어 제어 신호 전달이 끊기지 않음을 검증하였다. 본 연구는 전력설비 유지보수 차량의 안전 모니터링·설비 상태 진단·위험 대응 시스템 구현을 위한 실질적 기반을 확보하였으며, 향후 실제 현장 차량에 적용하여 장기 운영 안정성 검증과 통신 품질 최적화를 위한 추가 연구를 수행할 계획이다.
-
A Study on the Design of Gateway and Communication System for Intelligent Safety Module in Power Facility Maintenance Vehicles
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of Korean Society of Disaster and Security
Journal of Korean Society of Disaster and Security
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of Korean Society of Disaster and Security
Journal of Korean Society of Disaster and Security









